|
|
 |
The STRENGTH of MATERIALS range of Hi-Tech Education equipment enables clear and comprehensive learning of Materials and their Properties covering a variety of theories and topics. An understanding of the way in which materials act and react, is fundamental when studying the application of loads on a variety of fixed or moving structures. The STRENGTH of MATERIALS form a comprehensive range of equipment, from fixed beams through to rotating machines apparatus, equally suitable for demonstration and experimental work.
All the STRENGTH of MATERIALS hardware operates in a standalone mode, with a large number being supplied with Data Acquisition Interfaces and Software.
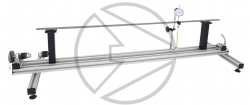
HSM1cD Advanced Beam Testing ApparatusAn unlimited range of beam experiments can be performed to measure support reactions, deflections and rotations of simply supported, fixed and two span continuous beams, simple and propped cantilevers, and sinking supports. |
 |
HSM4 Pendulum Impact Tester (4J)A sturdy unit for the study of notched bar impact strength of materials. A base plate with protective guard houses all the components. The base plate supports an anvil and pillar which have profiles for supporting the notched specimens prior to testing. A heavy hammer swings on a pre-defined radius. The initial energy of the hammer can be varied by changing the starting weight and/or height of the hammer. As the hammer swings through its radius, it impacts on the specimen and the distance it travels passed the specimen is measured on an integral scale. The release of the hammer is controlled with a hand operated plunger. A number of test specimens are provided in differing materials, with further specimens available separately. |
 |
HSM2 Torsion of BarsApparatus to understand and investigate directly the relationship between the torsional load applied to a round bar and the angular twist produced and how this relationship varies with the beam material and it’s cross sectional polar moment of area. Specimens are rigidly held in a clamp fixed to one end of the bench top base frame of the apparatus. |
 |
HSM7 Extension of SpringsSprings are used in engineering to store energy or to provide restoring forces. Both compression and tension (extension) springs may be encountered. The deflection of a spring depends on the load applied to it, an observation enshrined in Hooke's Law (Within the limit of proportionality, the strain is directly proportional to the stress producing it).Applications of springs are found in spring balances which indicate loads by measuring spring deflections and in car suspensions where they absorb energy caused by wheel vertical movement due to potholes and bumps. The HSM7 apparatus is designed to be mounted to a rigid vertical support approximately 1.5metres above floor level. It is used to test tension springs up to 200mm in length. The maximum spring diameter is 38mm. |
|
HSM8 Compression of SpringsSprings are used in engineering to store energy or to provide restoring forces. Both compression and tension (extension) springs may be encountered. The deflection of a spring depends on the load applied to it, an observation enshrined in Hooke's Law (Within the limit of proportionality, the strain is directly proportional to the stress producing it). Applications of springs are found in spring balances which indicate loads by measuring spring deflections and in car suspensions where they absorb energy caused by wheel vertical movement due to potholes and bumps. |
|
HSM10 Curved BarsThe theoretical deflections of curved shapes are most easily found by applying strain energy ideas, such as Castigliano's first theorem. The shapes chosen in this apparatus provide a relatively easy introduction to the use of such techniques. |
 |
HSM11 Combined Bending and TorsionThe object of this experiment is to determine what levels of combined bending and torsion cause elastic failure in different materials, and to compare them with various theories of failure. The apparatus uses specially machined ‘necked’ specimens which are clamped at one end to the base plate and at the other end to a counterbalanced circular loading plate. |
 |
HSM15 Critical condition of StrutsA piece of material in compression is called a strut. If it is short and stubby it will fail by compressive stress, but if it is slender the failure mode is that of buckling. The load at which the strut buckles depends on the way in which the ends are restrained. Built-in ends resist buckling more than ends which are free to move. The apparatus shows how the buckling mechanism occurs, and the influence of the end restraint. |
 |
HSM16 Torsion of a Spiral SpringSpiral springs are used to provide a resisting or restoring torque to a shaft when it is rotated through an angular displacement. They exhibit similar stiffness characteristics to linear springs, except that the effect is one of torque rather than force. The stiffness of a spiral spring depends on its physical dimensions and the rigidity of the steel strip from which it is formed. |
 |
HSM18 Electrical Resistance Strain GaugeThe apparatus has been designed to illustrate the basic features of electrical resistance strain gauges and their application in measuring bending and torsion. A cantilever has a single gauge bonded onto its surface, and an identical gauge is fixed to an unstressed piece of the same material for temperature compensation. |
 |
HSM19 Rotating Fatigue MachineThis apparatus has been designed to introduce students to the effects of fatigue. A motor rotates a specimen through a gear and pulley arrangement which can be adjusted. During the rotation the specimen is subject to sinusoidal variation of bending stress. |
 |
HSM19D Rotating Fatigue Machine (Digital)This apparatus has been designed to introduce students to the effects of material fatigue. A motor rotates a specimen through a gear and pulley arrangement which can be adjusted. During the rotation the specimen is subject to sinusoidal variation of bending stress. Loads are applied to the test specimen using a screw jack loading mechanism with integral load cell. When failure occurs, a microswitch stops the motor and the cycles to failure are registered on a revolution counter. A safety guard shields all rotating parts. The apparatus is mounted on a heavy base plate. Specially machined necked test specimens are provided. |
 |
HSM20 Alternating Bending Fatigue MachineThe HSM20 Alternating Bending Fatigue Machine is a further evolution of the popular HSM19 Rotating fatigue Machine. Rather than rotating a specimen to fatigue failure, the HSM20 induces an alternating displacement to the free end of a cantilevered test specimen in order to fatigue fail the part. A heavy base plate houses the control box, motor, fluctuating components, test specimen and digital counter. All these parts are enclosed by a transparent safety guard, which ensures rotating components are kept away from the user but full view of parts and count is kept. |
 |
HSM30 Unsymmetrical Cantilever ApparatusThis apparatus allows the vertical and horizontal deflections of the free end of a test specimen to be measured when loading occurs along a principle axis or at a known angle. |
 |
HSM31 Torsion Testing Machine (30Nm)A sturdy bench mounted unit for studying applied torque against angle of twist, specimen failure, and test graphs. Torque is applied via the moment head to differing material test specimens using hand operated worm and wheel gearbox. |
 |
HSM32 Thick Cylinder ApparatusA heavy bench top unit for studying the stress and strain in a thick walled cylinder under internal pressures. A thick walled cylinder is mounted between two support blocks. Internal seals create oil sealing. |
 |
HSM33 Thin Cylinder ApparatusA heavy bench top unit for studying the stress and strain in a thin walled cylinder under internal pressure. A thin walled cylinder is mounted between two support blocks. Internal pistons and seals create oil sealing. |
 |
HSM34 Creep Testing MachineA sturdy bench top mounted unit for studying the affect of creep on different material test specimens. Necked test specimens are held vertically in position on special clamps, which do not induce bending during loading. A lever arm transmits the load from a load hanger and weights into the specimen and the lever arm has a counter balance weight to ensure the lever arm self weight is calibrated out. |
 |
HSM35 Torsion and Deflection Testing ApparatusThis bench top unit allows a variety of experiments to be undertaken to investigate test specimens under torsional loading and bending loading within their elastic limits. The students cover topics involving bending moment equation, torsional rigidity, modulus of rigidity, angle of twist, and create graphs and compare actual measured values with theoretical values using formulae and theory provided. |
 |
HSM38 PolariscopeThe HSM38 polariscope is a bench top mounted frame which allows the study of stress patterns and photoelasticity resulting from geometrical changes in loaded mechanical models. The frame has integral slides into which fit quarter wave plates and polarisation filters. These plates and filters can be rotated through 90° to vary the colourisation seen by the user. The frame can sit on top of a light box (not supplied) or overhead projector (not supplied). Rubber mounting feet enable it to sit firmly onto the light source. |
 |
HSM40 Torsion Testing Machine (200Nm)A sturdy bench top mounted unit for torsion testing of varying material test specimens to failure/destruction. Using a speed controlled electric motor torque is applied through the drive gearboxes rigidly attached at one end of the base frame. |
 |
HSM41 Pendulum Impact Tester (25J)A unit for the study of notched bar impact strength tests. A sturdy base plate with protective guard houses all the components. The base plate has an integral anvil and pillar which have profiles for supporting the notched specimens. |
 |
HSM43 Torsion Testing Machine (100Nm)An apparatus for manually applying torque to test specimens until failure occurs. Torque is applied to differing material test specimens using hand operated gearbox. |
 |
HSM44 Hydraulic Universal Material Tester (50kN)This material tester is a bench top unit for training purposes. Simple operation and robust construction make the unit suitable for student experiments. |
 |
HSM45 Transmitted Light PolariscopeThe HSM45 polariscope is a bench top mounted frame which allows the study of stress patterns and photoelasticity resulting from geometrical changes in loaded mechanical models. Photoelastic analysis is achieved by passing light through the mechanical stress models while a tensile load is applied. The frame has the polarisation filter and quarter wave plate mounted to rotational frames. These frames allow the rotational angle of the plates and filters to be adjusted and hence vary the colourisation seen by the user. |
 |
HSM48 Round Diaphragm ApparatusSturdy, compact, self contained bench top unit for determining the surface strains and deflections of a flexible diaphragm under varying pressures. An aluminium diaphragm is clamped rigidly around its outer edge, creating a volume underneath its surface into which oil is filled. |
 |
HSM51 Rockwell/Brinel combined Hardness TesterThis combined hardness tester is designed for measuring hardness of metals and alloys of all types (hard and soft). The specimens can be flat, or round and irregular in shape. The hardness tester is bench mounted unit. The principle of operation is based around a lever and weights. |
 |
HSM53 Vickers Hardness TesterThis accurate bench top unit is designed specifically for Vickers hardness testing. The testing range is very wide, from soft metal such as lead, upto the hardest, like hardened steel. |
 |
HSM55 Pendulum Impact Tester (300J)The HSM55 Pendulum Impact Tester consists of a solid base and pillar with a pendulum, specimen support anvil, brake and the measuring dial. The apparatus has two starting positions. An upper position for Charpy testing and a lower position for Izod. On release, the pendulum swings down to break the specimen and the energy absorbed in doing so is measured as the difference between the height of the drop before rupture and the height of rise after rupture of the test specimen. The absorbed energy is read from the digital display situated on the top of the pillar. |
 |
HSM56 Extension and Compression of SpringsA wall mounted vertical bracket houses two independent mechanisms side by side for testing tension and compression springs. The left hand side tests tension springs whilst the right hand side tests compression spring. |
 |
HSM57 Loading and Buckling of StrutsA sturdy bench or floor mounted apparatus for testing of struts under compressive loads. Supplied test specimens of various lengths and cross section are placed into the unit and a compressive load applied through the screw jack mechanism. |
 |
HSM58 Universal Materials Tester (20kN)Universal Material Tester allowing tests to undertaken on specimens in Tension, Compression, Shear, and Bending. The apparatus comes supplied with a Digital Interface and Data Acquisition Software as standard. A variety of optional modules are available which covers tests such as Brinell Hardness, Cupping, Spring Testing, and many more. |
 |